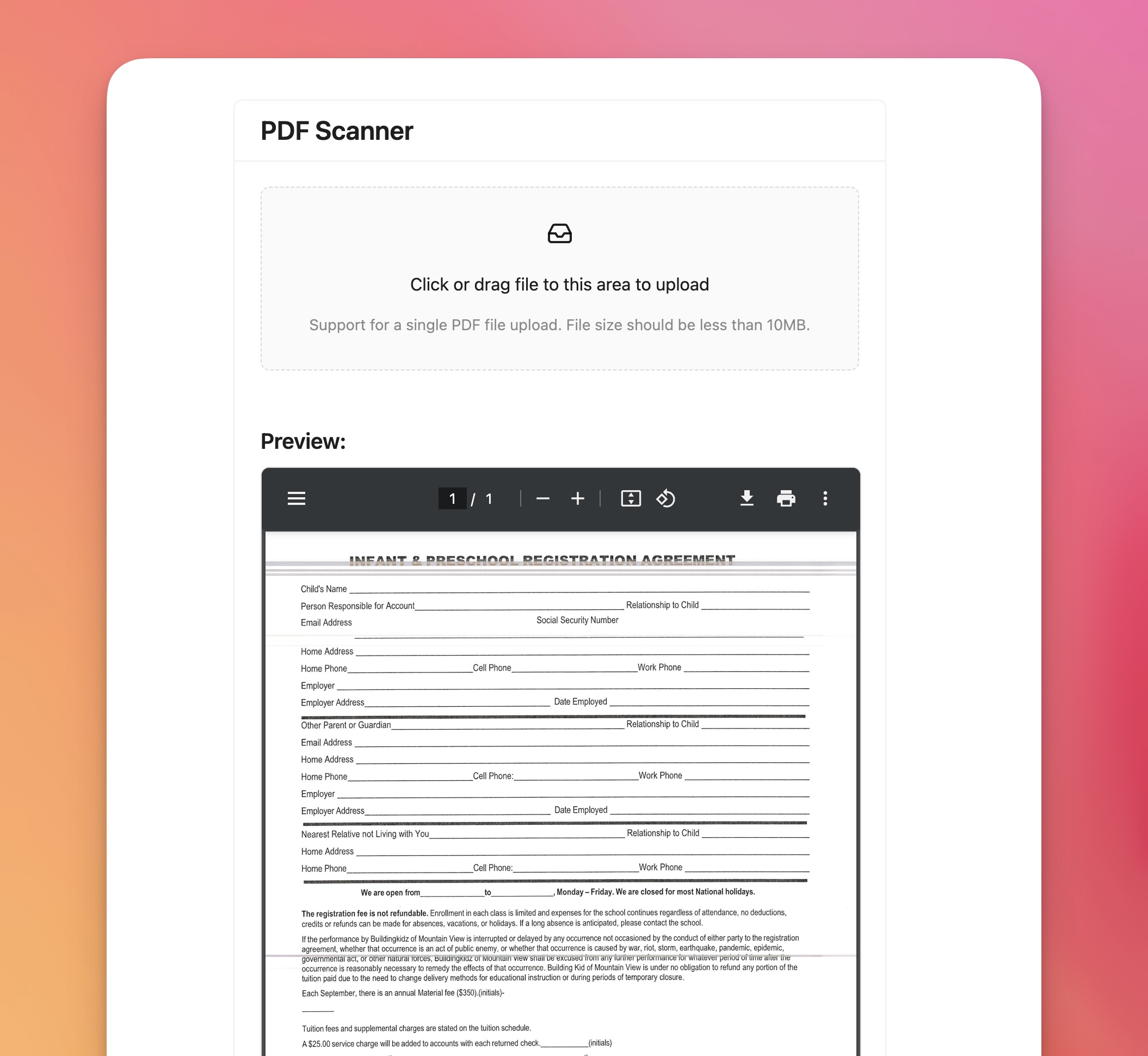
Scan To PDF
Scan your files using AI and remove the background.Click or drag file to this area to upload
Support for a single PDF file upload. File size should be less than 10MB.
What is a Scanner?
Scanners have become an integral part of both professional and personal workflows, converting hard copies of documents and images into digital formats. As the digital age continues to evolve, understanding what scanners are and how they work can be beneficial for anyone looking to streamline processes or preserve important materials.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Types of Scanners
- How Scanners Work
- Benefits of Using Scanners
- Choosing the Right Scanner
- Conclusion
Introduction
A scanner is a device that captures images from photographic prints, posters, magazine pages, or other sources for digital processing. Often used in various fields such as education, business, and photography, scanners serve to digitize physical documents and images for easier storage, editing, and sharing.
Types of Scanners
Flatbed Scanners
Flatbed scanners are the most common type of scanner. They consist of a glass pane over which the document or image is placed, and a lid to hold it flat. The scanning element moves beneath the document to capture the image.
- Pros: Suitable for scanning books, photographs, and multiple types of documents.
- Cons: Tend to be bulky and require a flat, stable surface.
Sheetfed Scanners
Sheetfed scanners differ from flatbed scanners in that the document is fed into the scanner rather than laid on a glass pane. These scanners are excellent for scanning multiple pages quickly.
- Pros: Ideal for scanning large volumes of documents quickly.
- Cons: Less versatile when it comes to scanning bound books or very thick items.
Handheld Scanners
Handheld scanners are portable devices that the user manually moves over the document they wish to scan. These are often used for smaller documents or specific areas of interest.
- Pros: Highly portable and flexible.
- Cons: Require a steady hand for accurate scanning and may not be ideal for larger documents.
Photo Scanners
Photo scanners are specialized devices designed explicitly for high-resolution scanning of photographs. They often come with features to restore color and remove dust and scratches.
- Pros: Provides high-resolution scans perfect for photographic work.
- Cons: Often more expensive and less suited for scanning text documents.
Portable Scanners
Portable scanners are compact and easy to carry, intended for on-the-go scanning needs. These usually connect via USB or Bluetooth to other devices for immediate transfer.
- Pros: Great for travelers and those needing quick scans on the move.
- Cons: Limited functionality compared to larger, more powerful scanners.
3D Scanners
3D scanners capture the shape of objects, convert them into 3D models, and are often used in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and art.
- Pros: Allows capturing of complex shapes and sizes for 3D printing or analysis.
- Cons: Generally expensive and require more technical expertise to use.
How Scanners Work
Scanners operate by using a light source to illuminate the document, which is then reflected back through a series of mirrors and lenses onto a sensor, usually a Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) or a Contact Image Sensor (CIS). This sensor converts the light into electrical signals, which are then digitized to form an image.
Benefits of Using Scanners
- Digital Storage: Easily store large quantities of documents electronically, saving physical space.
- Improved Access: Quickly retrieve and share documents and images via email or cloud storage.
- Editing Capabilities: Once digitized, documents and images can be edited, enhanced, or altered using various software applications.
- Preservation: Helps in preserving old documents and photos by creating digital backups.
- Environmental Benefits: Reduces the need for paper copies, contributing to a greener office environment.
Choosing the Right Scanner
When selecting a scanner, consider the following factors:
- Purpose: Determine whether you need the scanner for general document scanning, photo scanning, or more specialized needs.
- Resolution: Higher resolution scanners are essential for photo and image scanning but may not be necessary for text documents.
- Speed: If you need to scan large volumes of documents regularly, opt for a high-speed scanner.
- Size and Portability: Choose a size that fits your workspace and decide if portability is a requirement.
- Software Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your operating system and any image or document editing software you might use.
Conclusion
Scanners are versatile tools that bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds. Whether for personal use or professional applications, understanding the different types of scanners and their functionalities can help you choose the right device for your needs. By digitizing your documents and images, you not only streamline your processes but also contribute to more efficient and sustainable practices.
Ensure you're making the most of these powerful devices by selecting one that aligns with your specific requirements, be it high-resolution photo scanning or fast, bulk document digitizing. Knowing your needs and the capabilities of each type of scanner will lead to more productive and effective document management.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly optimize your understanding and use of scanners, making your digital document management more seamless and efficient.
Download Now
The Slikest Files Experience Ever Made