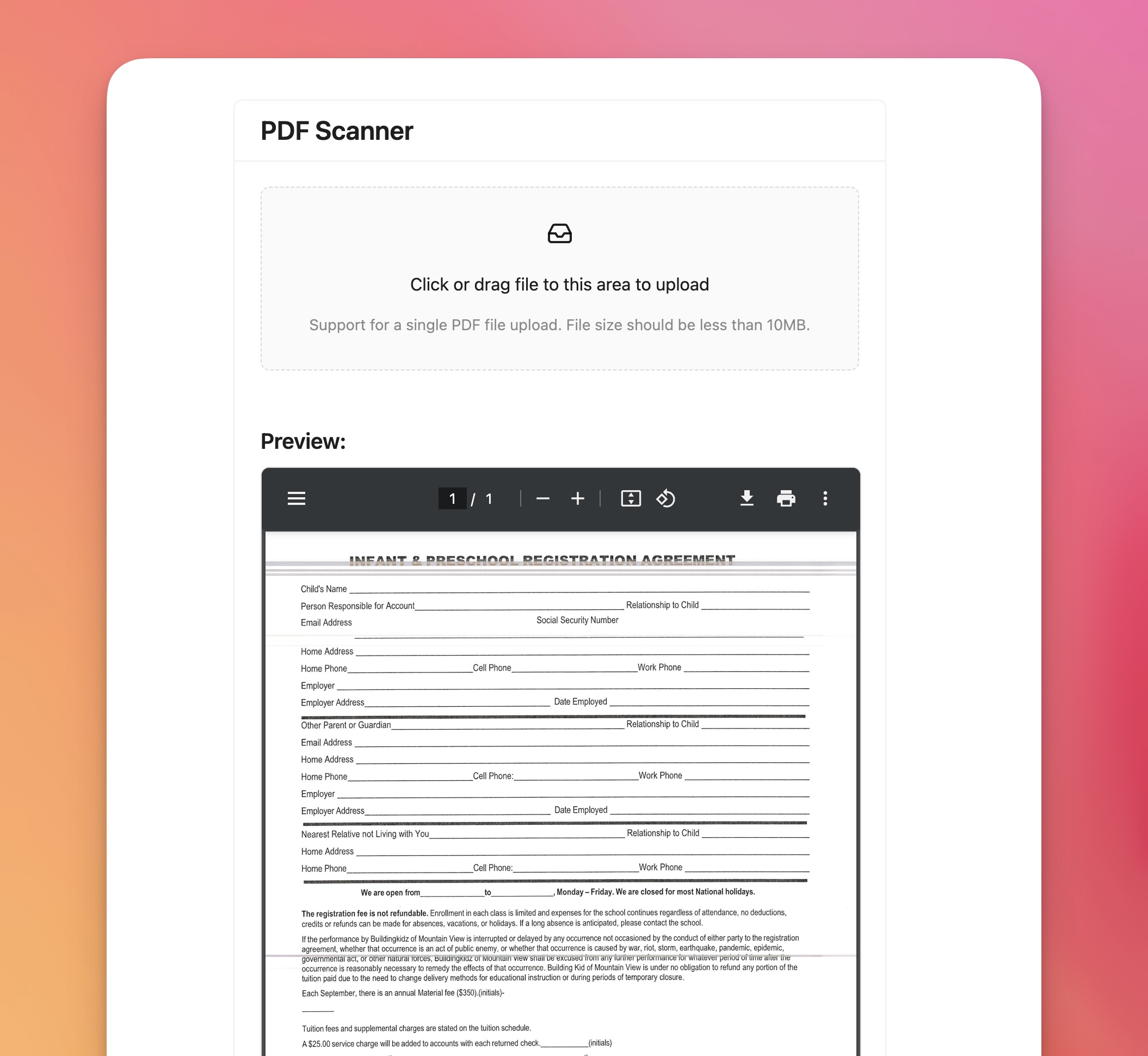
Scan To PDF
Scan your files using AI and remove the background.Click or drag file to this area to upload
Support for a single PDF file upload. File size should be less than 10MB.
What is a Scanner?
In today's digital age, scanners play a crucial role in bridging our physical and digital worlds. Scanners are devices that convert physical documents, images, or objects into digital format, making it easier to store, share, and process information. Whether you're a student, professional, or hobbyist, understanding the basic and advanced functionalities of a scanner can greatly enhance your productivity. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the different types of scanners, how they work, and their numerous applications.
Types of Scanners
1. Flatbed Scanners
Flatbed scanners are perhaps the most commonly used type of scanner. They feature a flat surface or glass platen where the document or object to be scanned is placed face-down. A light source and sensor move beneath the glass to capture the image.
Key Features:
- Suitable for scanning a variety of documents, photographs, and books.
- High-resolution scanning for detailed images.
- Relatively slow compared to other types but offers superior quality.
2. Sheet-fed Scanners
These scanners are designed to handle multiple pages at once. The document is fed through the scanner, which captures the image as it passes through.
Key Features:
- Ideal for scanning large volumes of documents quickly.
- Less suitable for delicate or fragile documents.
- Generally lower resolution compared to flatbed scanners.
3. Handheld Scanners
Handheld scanners are portable devices that you manually move across the document to capture an image. They are useful for scanning small documents or specific sections of a larger document.
Key Features:
- Portability and ease of use.
- Ideal for scanning smaller items or text snippets.
- Lower resolution and potential for scanning errors if not moved steadily.
4. Drum Scanners
Drum scanners use a photomultiplier tube (PMT) to capture images, offering superior quality and detail. They are often used in professional settings such as graphic design and photography.
Key Features:
- High-resolution, color accuracy, and detail.
- Typically very expensive and used by professionals.
- Not suitable for everyday scanning tasks.
How Scanners Work
Imaging Sensor
The core component of any scanner is the imaging sensor. Commonly used types include Charge-Coupled Devices (CCD) and Contact Image Sensors (CIS). CCDs are known for their high image quality but are bulkier, while CIS scanners are more compact but may offer lower quality.
Light Source
The light source illuminates the document from beneath the glass platen. LED, Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps (CCFL), and Xenon lamps are commonly used, with LEDs being the most energy-efficient.
Optical Resolution
This refers to the amount of detail the scanner can capture, measured in DPI (dots per inch). Higher DPI results in more detailed scans but also larger file sizes. For general document scanning, a resolution of 300 DPI is adequate, whereas photographs may require up to 1200 DPI or more.
Scanning Software
Most scanners come with bundled software that offers various functionalities such as image enhancement, Optical Character Recognition (OCR), and file management. Advanced software solutions offer better image quality and additional features.
Applications of Scanners
1. Document Management
Scanners are essential tools in modern offices for converting paper documents into digital files, which can then be stored, managed, and retrieved more efficiently. OCR technology further allows for searchable documents.
2. Archiving and Preservation
Historical documents, photographs, and artworks can be digitized to preserve them for future generations. Museums and libraries frequently use high-resolution scanners for this purpose.
3. Graphic Design and Publishing
High-quality images are crucial in graphic design, advertising, and publishing. Scanners help in digitizing photographs, artwork, and other visual materials.
4. Educational Uses
Students and educators rely on scanners to digitize textbooks, notes, and other educational materials for easier dissemination and study.
5. Medical and Scientific Applications
Scanners are used in medical fields to digitize patient records and in scientific research to capture detailed images of samples.
Benefits of Using Scanners
Efficiency and Productivity
Digitizing documents reduces the need for physical storage and makes information retrieval faster and more efficient.
Improved Collaboration
Digital files can be easily shared and accessed by multiple people, improving collaboration and communication within teams.
Enhanced Security
Digital files can be encrypted and backed up, offering better security compared to physical documents which are susceptible to damage and loss.
Environmental Impact
Reducing reliance on paper through digitization is an eco-friendly practice, contributing to environmental conservation efforts.
Conclusion
Scanners are indispensable tools that significantly streamline the process of converting physical documents and images into digital formats. From enhancing productivity in offices to preserving historical artifacts, scanners serve a myriad of applications across various industries. Understanding the different types of scanners and their functionalities helps in choosing the right device tailored to your specific needs.
For those interested in exploring the latest models and software solutions, companies like Slik Safe offer state-of-the-art options that ensure high-quality scans and efficient image management.
FAQs
1. What is the best type of scanner for home use? Flatbed scanners are generally recommended for home use due to their versatility in scanning various types of documents and photos.
2. Can I scan documents directly to cloud storage? Many modern scanners offer integrated cloud storage options, allowing you to scan directly to services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and more.
3. Is OCR technology reliable for converting text documents? OCR technology has significantly improved and is highly reliable for converting text documents into editable and searchable formats. However, accuracy may vary based on the quality of the original document.
Keywords: Scanner, Flatbed Scanner, Sheet-fed Scanner, Handheld Scanner, Drum Scanner, Digital Imaging, OCR, Document Management
Meta Description: Discover what a scanner is and how it works. Learn about different types of scanners, their applications, benefits, and tips for choosing the best one for your needs.
By adhering to these SEO and content guidelines, this blog aims to provide comprehensive information on scanners, helping readers make informed decisions while enhancing their digital workflows.
Download Now
The Slikest Files Experience Ever Made