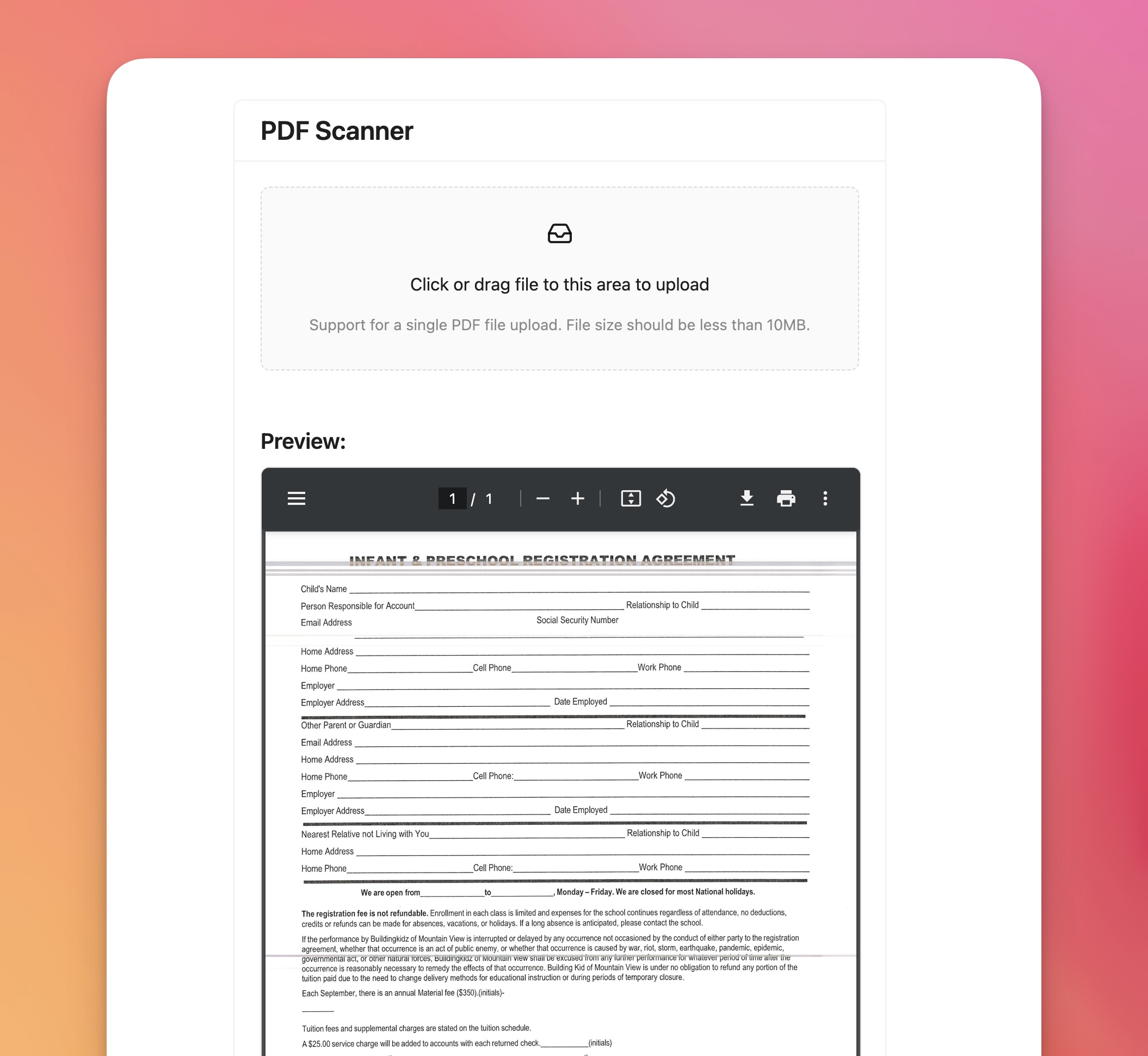
Scan To PDF
Scan your files using AI and remove the background.Click or drag file to this area to upload
Support for a single PDF file upload. File size should be less than 10MB.
A Comprehensive Guide to Scanning: Everything You Need to Know
In the digital age, the ability to scan documents, photos, and even 3D objects has become increasingly important. Whether you're a student, professional, or hobbyist, understanding the ins and outs of scanning can enhance your productivity and streamline your workflow. This comprehensive guide will cover the basics of scanning, its various types, and provide tips for achieving the best results.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Scanning
- Types of Scanners
- Why Scan?
- How to Scan Documents
- Best Practices for Scanning
- Common Scanning Issues and Troubleshooting
- Conclusion: Simplifying Your Workflow with Scanning
Introduction to Scanning
Scanning involves converting physical documents, photographs, or objects into digital formats. This process can be incredibly helpful for preserving important paperwork, sharing information, or creating digital backups. Scanning has applications in various fields, from medical imaging to art digitization.
Types of Scanners
Understanding the different types of scanners can help you choose the right one for your specific needs.
Flatbed Scanners
Flatbed scanners are the most common type and are ideal for scanning photos, documents, and books. They have a glass surface where you place the item to be scanned. The scanner head moves underneath the glass to capture the image.
Sheet-fed Scanners
Perfect for office environments, sheet-fed scanners automatically feed documents through the scanning mechanism. They are efficient for scanning multiple pages quickly but are not suitable for thick or bound items.
Handheld Scanners
Handheld scanners are portable devices that you manually move over the item to scan. They are useful for on-the-go scanning but may require a steady hand to achieve quality results.
Drum Scanners
Used primarily in professional printing and publishing, drum scanners offer the highest quality scans. They use photomultiplier tubes to capture images with exceptional detail and color accuracy.
3D Scanners
3D scanners capture the shape and texture of three-dimensional objects. They are widely used in manufacturing, healthcare, and virtual reality applications.
Why Scan?
Scanning offers several advantages:
- Digital Storage: Reduce physical clutter and store documents digitally.
- Preservation: Protect important documents and photos from wear and tear.
- Sharing: Easily share documents and images via email or cloud services.
- Searchability: Digital documents can be text-searched using Optical Character Recognition (OCR).
- Security: Digital backups provide an extra layer of security against physical damage or loss.
How to Scan Documents
Follow these steps to scan documents efficiently:
- Prepare Documents: Remove any staples or paper clips and ensure the document is clean and flat.
- Select Scanner and Software: Choose an appropriate scanner and install any necessary software.
- Place Document: Align the document on the scanner bed or feed it into the sheet-fed scanner.
- Choose Settings: Adjust settings such as resolution, color mode, and file format.
- Scan: Initiate the scanning process through the software.
- Save and Organize: Save the scanned files in a well-organized folder structure with descriptive file names.
Best Practices for Scanning
To achieve the best scanning results, consider the following tips:
- Resolution: Use a resolution of at least 300 DPI (dots per inch) for documents and 600 DPI for photos.
- Color Mode: Choose grayscale for text documents and color mode for photos or colored documents.
- File Formats: Save documents in PDF or TIFF for high quality and photos in JPEG or PNG.
- Maintenance: Regularly clean the scanner glass and calibrate your scanner to maintain quality.
Common Scanning Issues and Troubleshooting
Encountering problems while scanning is not uncommon. Here are some solutions to common issues:
- Blurry Images: Ensure the document is flat and the scanner is properly calibrated.
- Lines on Scans: Clean the scanner glass and check for any debris on the scanner head.
- Scanner Not Recognized: Verify connections and reinstall the scanner driver.
- Slow Scanning: Lower the resolution or check for software updates.
Using Third-Party Software for Scanning
If you don't have access to a physical scanner, there are several third-party software options available that can turn your smartphone or computer into a powerful scanning tool. Here are some popular choices:
Smartphone Apps
- Adobe Scan: Available for both Android and iOS, Adobe Scan allows you to capture documents, receipts, notes, and more. It automatically detects edges, performs OCR, and saves scans as PDF files.
- CamScanner: This app offers features like auto-enhancement, smart cropping, and OCR. It supports saving scans in various formats and sharing them via email or cloud services.
- Microsoft Office Lens: Ideal for capturing whiteboards, documents, and business cards. It integrates with OneNote and OneDrive, making it easy to save and organize your scans.
- Slik Scan: A web-based tool that works on both Android and iOS devices. Slik Scan allows you to scan documents directly from your web browser without the need for additional downloads. It offers features like edge detection, auto-capture, and the ability to save scans in various formats.
Conclusion
Scanning is a versatile and essential tool that can greatly simplify your workflow. By understanding the different types of scanners and following best practices, you can achieve high-quality scans that are easy to store, share, and manage. Whether you're digitizing old photos or converting important documents, scanning offers a practical solution for preserving and organizing your physical and digital assets.
Other free apps by Slik Safe
Download Now
The Slikest Files Experience Ever Made